The Dynasties and Rulers of Chinese History
China's five-thousand-year history has seen countless changes of dynasties, among which the best-known are the nine great unified dynasties: Qin, Han, Jin, Sui, Tang, Song, Yuan, Ming and Qing.
The Qin Dynasty was the first great unified dynasty in Chinese history. Before the founding of the Qin Dynasty, the historical period is known as the pre-Qin period. Excluding the era of ancient culture, the pre-Qin period mainly experienced the Xia, Shang, and Zhou dynasties. Among them, the ancient Xia dynasty has a history of more than four thousand years since its founding by the great Yu, the legendary hero who controlled the floods, and who is credited with the creation of the Huaxia ethnic group. They are briefly presented below:
1.Xia Dynasty (2070 BC - 1600 BC): The Xia Dynasty was the first slave dynasty in China. Yu the Great established the Xia dynasty, and his son Qi ascended the throne, marking the beginning of hereditary succession to the throne.
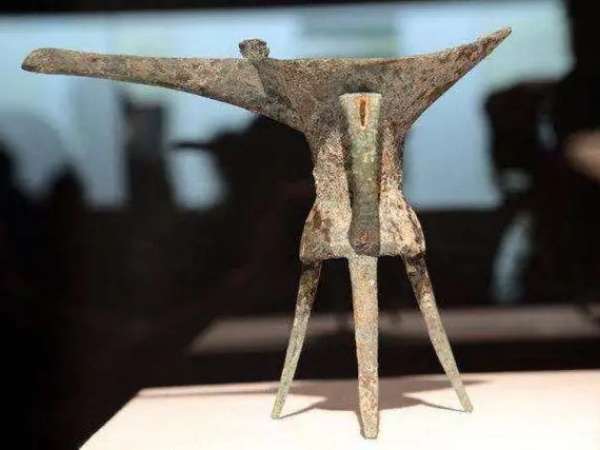

2.Shang Dynasty (1600 BC – 1046 BC): During the early period of the Shang Dynasty, the capital was moved several times, but in the middle of his period, King Pan Geng moved the capital to Yin, thus establishing stability , so the Shang Dynasty is also known as the Yin Dynasty.
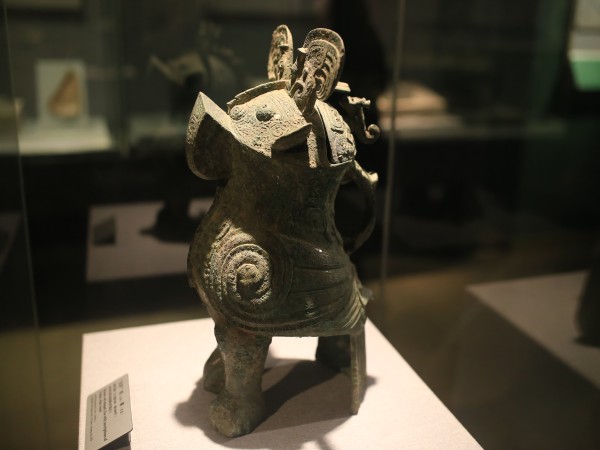

3.Western Zhou (1046 BC - 771 BC): King Wu of Zhou defeated King Zhou of Shang and established the Zhou dynasty, which was the third slave dynasty of China.
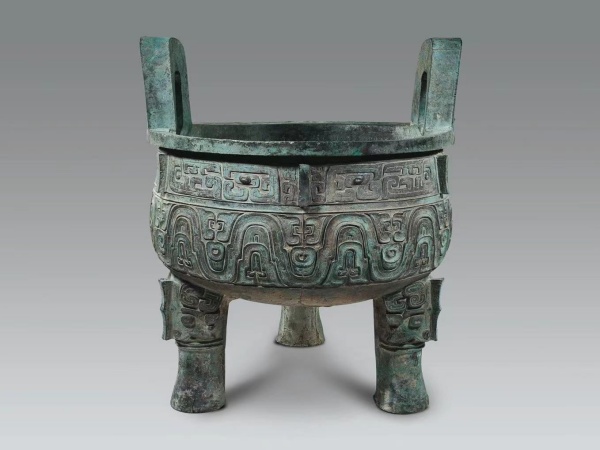

4.Eastern Zhou (770 BC – 221 BC): The Zhou dynasty divided into Western Zhou and Eastern Zhou, with King Wu of Zhou's son, King Cheng of Zhou, ascending the throne in Western Zhou, while King Ping of Zhou ascended the throne in Eastern Zhou, which was divided into the Spring and Autumn and Warring States periods.
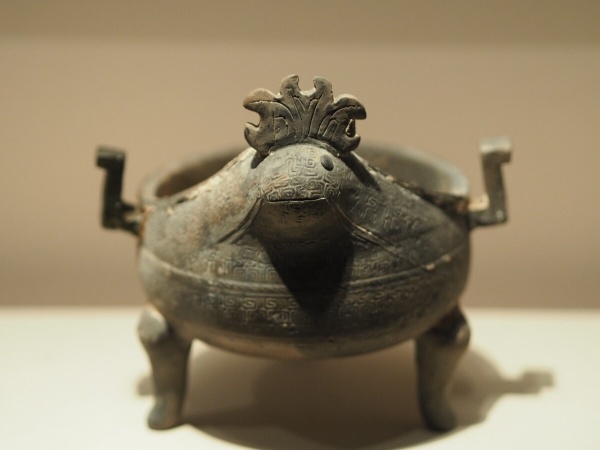

5.Qin Dynasty (221 BC - 206 BC): The Qin Dynasty was the first great unified dynasty in Chinese history, developed from the State of Qin in the Warring States period. King Qin Shi Huang united the six states and established a centralized and unified multi-ethnic state.
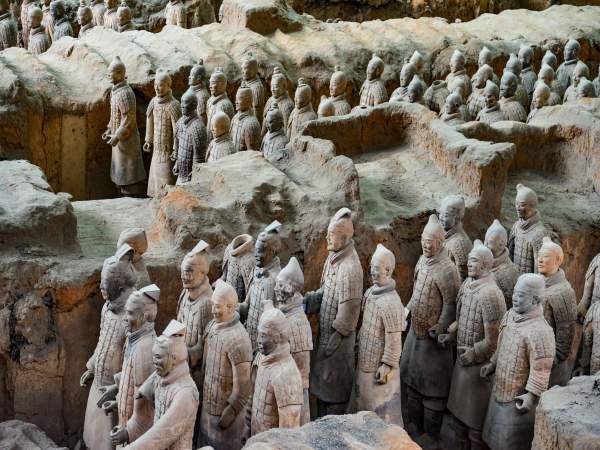

6.Han Dynasty (206 BC – 220 AD): The Han Dynasty was the second great unified dynasty in Chinese history. After Liu Bang conquered the country, he gradually eliminated the feudal kings of different surnames and appointed them as feudal princes. At the beginning of the Han Dynasty, there was an economic decline, but during the reign of Emperor Wu of Han, the era of Guangwu and Wending prosperity began, and the Han Dynasty entered its heyday, marking the first peak of development of the Han Dynasty. feudal dynasties.
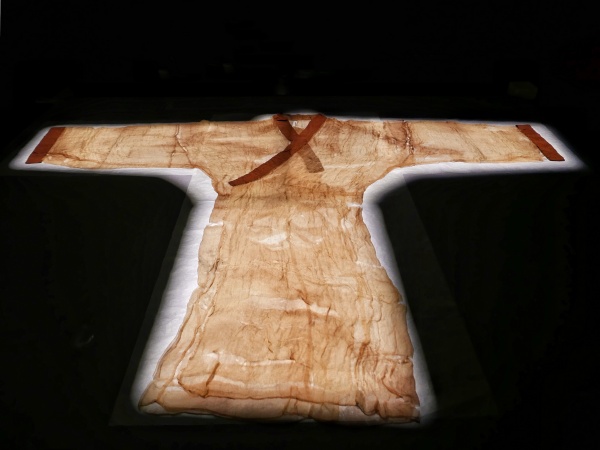

7.Three Kingdoms Period (220 AD - 280 AD): The Three Kingdoms period was composed of the states of Cao Wei, Shu Han and Wu Dong, which fought a protracted war for several decades, and finally, in the In 280 AD, Jin unified the east and the west, thus uniting the country.
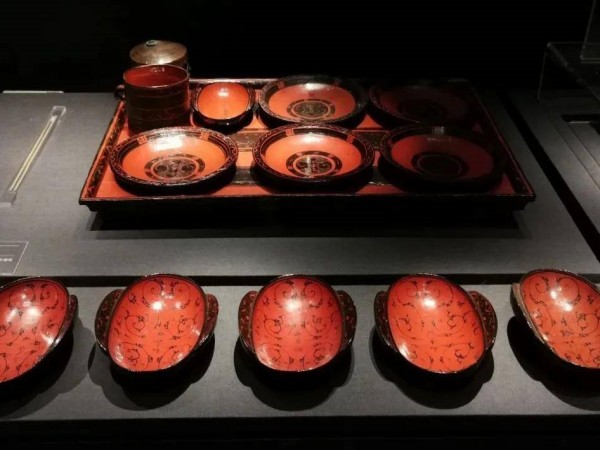

8.Period of the Southern and Northern Dynasties (420 AD - 589 AD): During the period of the Southern and Northern Dynasties, the Southern dynasties of Song, Qi, Liang and Chen, and the dynasties of the Northern Wei, Eastern Wei, Western Wei, Northern Qi and Northern Zhou, known collectively as the "Southern and Northern Dynasties".
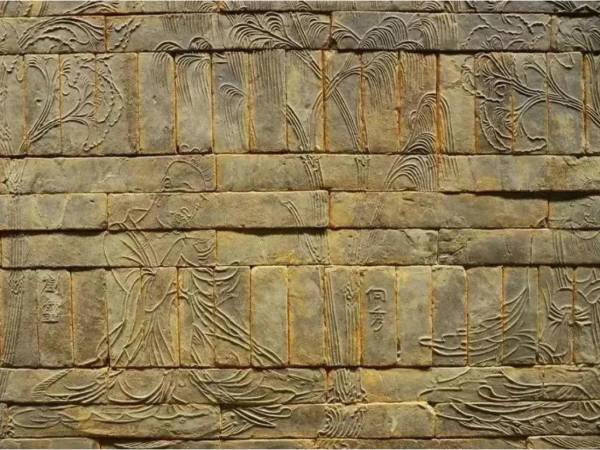

9.Sui Dynasty (581 AD – 618 AD): The Sui Dynasty was the third great unified dynasty in Chinese history. Emperor Wen of Sui, Yang Jian, established the Sui dynasty and carried out a series of reform policies that led to social stability and economic prosperity, ushering in the Kaihuang era.

10.Tang Dynasty (618 AD - 907 AD): The Tang Dynasty was the first prosperous dynasty in Chinese history and one of the most splendid. Emperor Taizong of Tang, Li Shimin, ushered in the Zhenguan era, while Emperor Xuanzong of Tang, Li Longji, ushered in the Kaiyuan era. The economy, politics and culture of the Tang Dynasty reached its peak.

11.Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period (907 AD - 960 AD): During the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period, the Later Liang, Later Tang, Later Jin, Later Han dynasties appeared successively. and later Zhou, known collectively as the "Five Dynasties", as well as the ten regional kingdoms.

12.Song Dynasty (960 AD – 1279 AD): The Song Dynasty is divided into the Northern Song Dynasty and the Southern Song Dynasty. The Northern Song Dynasty was established by Zhao Kuangyin, while the Southern Song Dynasty was established by Zhao Kuangyi, who implemented the abdication system and strengthened the centralization of power. The science, technology, economy and art of the Song Dynasty have diverse characteristics, and historians regard the Song Dynasty as the peak of ancient Chinese society.

13.Liao Dynasty (907 AD – 1125 AD): The Liao dynasty was a regime established by the Qidan tribe in northern China, which is divided into the Northern Liao and the Western Liao. The Liao dynasty established the Liao-Jin culture, which had a great influence on Chinese history in terms of politics, economy, and culture.
14.Western Xia (1038 AD – 1227 AD): The Western Xia was a regime established by the Xixia tribe in northwest China, divided into Northern Xia and Southern Xia. The Western Xia had unique characteristics in terms of culture, technology, and art, and also maintained complicated relations with the three regimes of Song, Liao, and Jin.

15.Jin Dynasty (1115 AD – 1234 AD): The Jin Dynasty was a regime established by the Jurchen tribe in northeastern China, divided into Northern Jin and Southern Jin. The Jin Dynasty had a great influence on China's politics, economy and culture, and its founder, Aguda, was a famous strategist and politician in Chinese history.

16.Yuan Dynasty (1271 AD – 1368 AD): The Yuan dynasty was a regime established by the Mongol tribe in northern China, with the capital at Dadu. During the Yuan Dynasty, the economy flourished, culture shined, and the country was unified, promoting communication and fusion between various ethnicities.

17.Ming Dynasty (1368 AD - 1644 AD): The Ming Dynasty was a regime established by the Han ethnic group in northern China. Emperor Zhu Yuanzhang implemented a series of policies, such as colonization and the establishment of the imperial examination system, and the founding of the Imperial Guard, strengthening the power of the state. In the second half of the Ming Dynasty, due to political corruption and natural disasters, the country suffered a decline in power.

18.Qing Dynasty (1644 AD - 1912 AD): The Qing Dynasty was a regime established by the Manchu tribe in northern China. At the beginning of the Qing Dynasty, a series of measures were implemented to strengthen the centralization of power, such as the establishment of the Eight Flags system and the promulgation of the ring road law. During the early period of the Qing Dynasty, the country was prosperous, but in the later period, due to political corruption and foreign invasions, the country's power declined.

19.Republic of China (1912 AD - 1949 AD): The Republic of China was established by the Kuomintang under the leadership of Sun Yat-sen, and gradually took control of the Chinese government after the Northern War.
20.People's Republic of China (1949 AD - present): The People's Republic of China is a socialist state of people's democratic dictatorship led by the Communist Party of China, established by the alliance of the working class, the peasant class, the urban petty bourgeois class and the nationalist class, under the system of multiparty political cooperation and consultation.
Today, we live in an era full of opportunities and challenges, as well as hope and change. In this era, we have witnessed the most rapid technological development and cultural fusion in human history, and we have experienced unprecedented diversity and inclusion. We need to face it with an open, innovative and pragmatic attitude, seize the opportunities, face the challenges and contribute to the future of humanity with our own efforts.













